Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Center of Mass, Exercise 1: OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Center of Mass, Exercise 1: OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 7: Center of Mass, Exercise 1: OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Practice Book for KVPY Aptitude Test - Stream SA Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Center of Mass, Exercise 1: OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS with Hints & Solutions
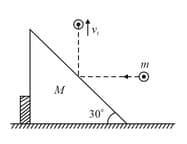
As shown in the figure a body of mass moving horizontally with speed hits a fixed smooth wedge and goes up with a velocity in the vertical direction. If angle of wedge is , the velocity will be
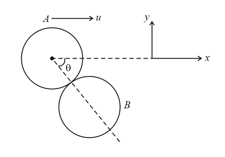
A small smooth disc of mass and radius moving with an initial velocity ' ' along the positive -axis collided with a big disc of mass and radius which was initially at rest with its centre at origin as shown in figure.
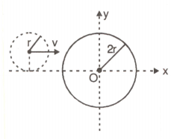
If the coefficient of restitution is then the velocity of the larger disc after the collision is
A ball of mass collides elastically with another identical ball at rest as shown in the figure. Initially, velocity of the ball is After collision
Two balls of the same mass are dropped from the same height onto the floor. The first ball bounces upwards from the floor elastically. The second ball sticks to the floor. The first applies an impulse to the floor of the second applies an impulse (for the duration of collision). Then the relation between both the impulses is,
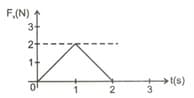
The given figure shows a plot of the time-dependent force acting on a particle in motion along the -axis. What is the total impulse delivered by this force to the particle from time to ?
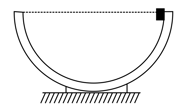
A very small cube is released from edge of a fixed hemispherical frictionless bowl whose radius is Which of the following is correct (mass of bowl mass of cube is ).
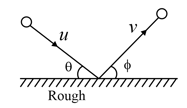
A ball is thrown onto a rough floor with speed at angle . If it rebounds with speed at the same angle . Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the floor and the ball. The coefficient of restitution,
Sand is falling on a flat car being pulled with constant speed. The rate of mass falling on the cart is constant. Then the horizontal component of force exerted by the falling sand on the cart,